React란?
React 컴포넌트는 render()라는 메서드를 이용하여 데이터를 입력받아 화면에 표시할 내용을 반환합니다.
1
| ReactDOM.render(<h1>Hello, world!</h1>, document.getElementById("root"));
|
React 소개 및 작동 원리
React 공식 문서 - Hello World
JSX는 객체를 나타냅니다.
1
| const element = <h1 className="greeting">Hello, world!</h1>;
|
Babel은 JSX를 컴파일하여 React.createElement()를 호출합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| const element = {
type: "h1",
props: {
className: "greeting",
children: "Hello, world!"
}
};
|
1
2
3
4
5
| const element = React.createElement(
"h1",
{ className: "greeting" },
"Hello, world!"
);
|
필요한 것만 업데이트하는 반응
React DOM은 요소와 하위 요소를 이전 요소와 비교하고 DOM을 원하는 상태로 가져 오는 데 필요한 DOM 업데이트 만 적용합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| function tick() {
const element = (
<div>
<h1>Hello, world!</h1>
<h2>It is {new Date().toLocaleTimeString()}.</h2>
</div>
);
ReactDOM.render(element, document.getElementById("root"));
}
setInterval(tick, 1000);
|
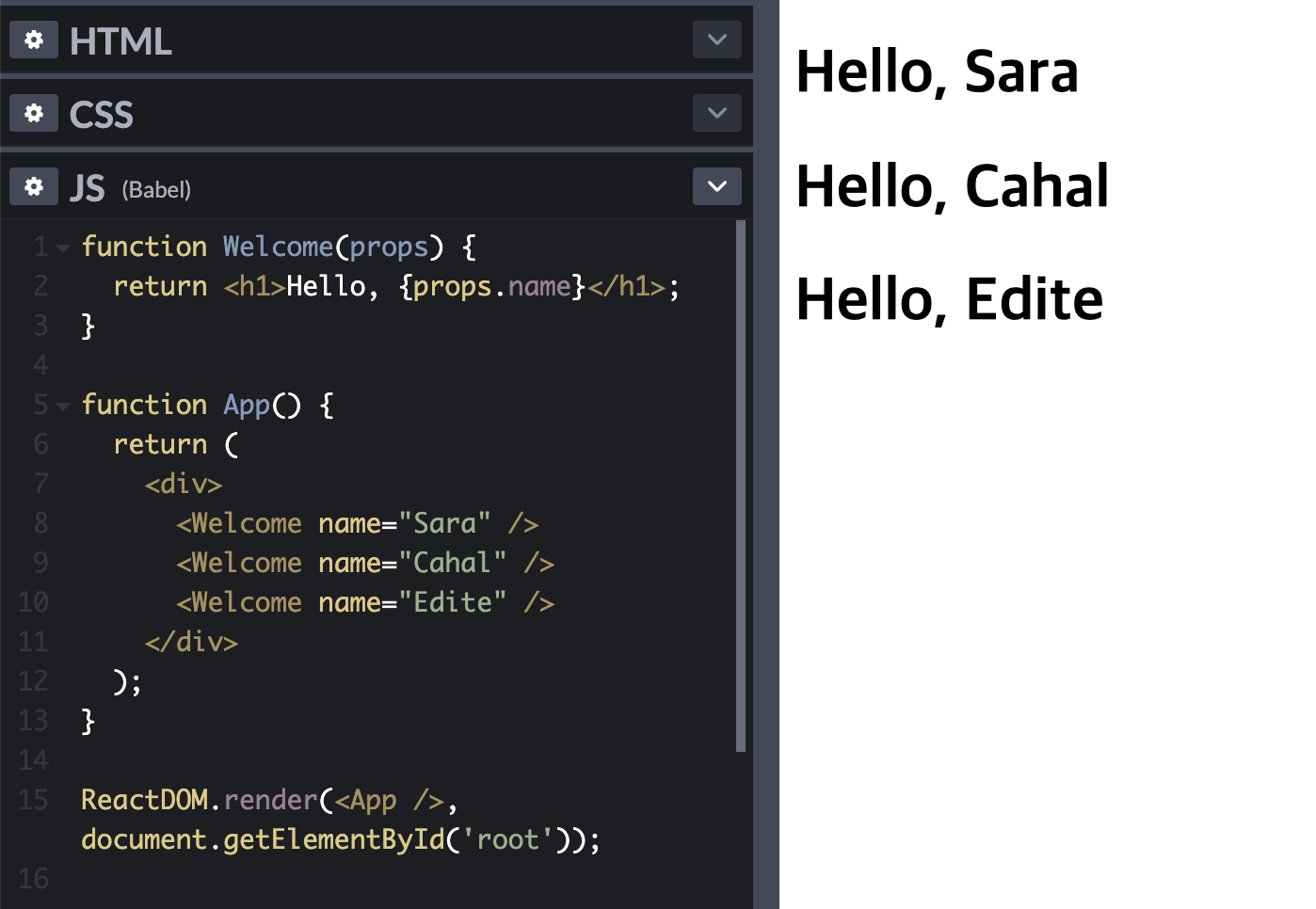
구성 요소 작성
React를 기존 앱에 통합하면 상향식으로 시작하여 점차적으로 뷰 계층 구조의 맨 위로 올라갈 수 있습니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| function Welcome(props) {
return <h1>Hello, {props.name}</h1>;
}
function App() {
return (
<div>
<Welcome name="Sara" />
<Welcome name="Cahal" />
<Welcome name="Edite" />
</div>
);
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById("root"));
|
이벤트 처리
preventDefault () 메서드는 취소 가능한 경우 이벤트를 취소합니다. 즉, 이벤트에 속한 기본 작업이 발생하지 않습니다. 예를 들어 다음과 같은 경우에 유용 할 수 있습니다.
- “제출”버튼을 클릭하면 양식이 제출되지 않습니다.
- 링크를 클릭하면 링크가 URL을 따라 가지 못하도록 합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| function ActionLink() {
function handleClick(e) {
e.preventDefault();
console.log("The link was clicked.");
}
return (
<a href="#" onClick={handleClick}>
Click me
</a>
);
}
|
JavaScript에서 클래스 메서드는 기본적으로 바인딩 되지 않습니다. ()와 같이 뒤에 없는 메서드를 참조하는 경우 onClick={this.handleClick} 해당 메서드를 바인딩 해야 합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
| class Toggle extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = { isToggleOn: true };
// This binding is necessary to make `this` work in the callback
this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this);
}
handleClick() {
this.setState((state) => ({
isToggleOn: !state.isToggleOn
}));
}
render() {
return (
<button onClick={this.handleClick}>
{this.state.isToggleOn ? "ON" : "OFF"}
</button>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<Toggle />, document.getElementById("root"));
|
조건부 렌더링
사용자가 로그인했는지 여부에 따라 이러한 구성 요소 중 하나를 표시 하는 구성 요소를 만듭니다. 현재 상태에 따라 <LoginButton /> 또는 <LogoutButton />이 렌더링 됩니다. 또한 Greeting 컴포넌트에서 <UserGreeting /> 또는 <GuestGreeting /> 을 렌더링합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
| function Greeting(props) {
const isLoggedIn = props.isLoggedIn;
if (isLoggedIn) {
return <UserGreeting />;
}
return <GuestGreeting />;
}
ReactDOM.render(
// Try changing to isLoggedIn={true}:
<Greeting isLoggedIn={false} />,
document.getElementById("root")
);
class LoginControl extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handleLoginClick = this.handleLoginClick.bind(this);
this.handleLogoutClick = this.handleLogoutClick.bind(this);
this.state = { isLoggedIn: false };
}
handleLoginClick() {
this.setState({ isLoggedIn: true });
}
handleLogoutClick() {
this.setState({ isLoggedIn: false });
}
render() {
const isLoggedIn = this.state.isLoggedIn;
let button;
if (isLoggedIn) {
button = <LogoutButton onClick={this.handleLogoutClick} />;
} else {
button = <LoginButton onClick={this.handleLoginClick} />;
}
return (
<div>
<Greeting isLoggedIn={isLoggedIn} />
{button}
</div>
);
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<LoginControl />, document.getElementById("root"));
|
Element Variable Example
Map 과 Key
key는 요소 목록을 만들 때 포함해야하는 특수 문자열 속성입니다. key는 주변 배열의 컨텍스트에서만 의미가 있습니다. <li>요소가 아닌 배열 ListItem의 <ListItem />요소에 키를 유지해야 합니다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| function ListItem(props) {
// Correct! There is no need to specify the key here:
return <li>{props.value}</li>;
}
function NumberList(props) {
const numbers = props.numbers;
const listItems = numbers.map((number) => (
// Correct! Key should be specified inside the array.
<ListItem key={number.toString()} value={number} />
));
return <ul>{listItems}</ul>;
}
const numbers = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5];
ReactDOM.render(
<NumberList numbers={numbers} />,
document.getElementById("root")
);
|